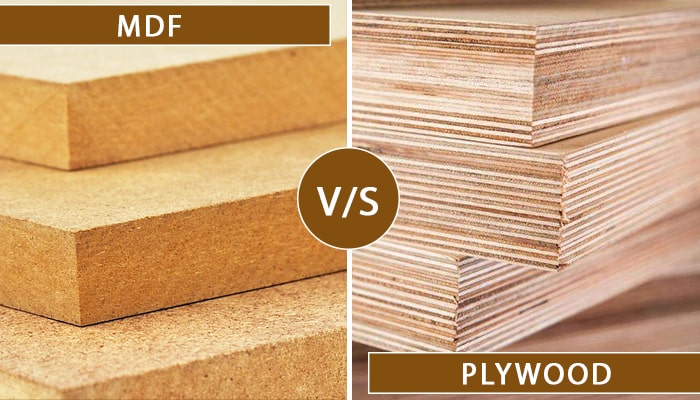
MDF and plywood are two of the most popular building materials today, especially for interior and exterior projects. Although both have their advantages, they are not interchangeable. So what makes the difference between MDF and Plywood, let’s find out with A1 Plywood!
1. What are MDF and Plywood?
1.1. MDF
Medium-density fiberboard (MDF) is a homogeneous mixture of wood fibers and urea-formaldehyde resin. It has smooth edges and surfaces, giving the appearance of a solid piece of material. MDF has a hard surface and is not resistant to moisture so it is useful for some structural applications but is mainly used indoors. If left untreated, MDF will absorb water like a sponge and swell, losing structural integrity in the process.
MDF covers a wide range of wood composites, but most of them share roughly the same properties. Here are some types of MDF that you may come across. Moisture-resistant MDF- Used in areas such as bathrooms where there is a constant risk of moisture. It can also be used in the kitchen. There are a few caveats about what you can skip that I’ll cover in a moment. These boards are usually green.
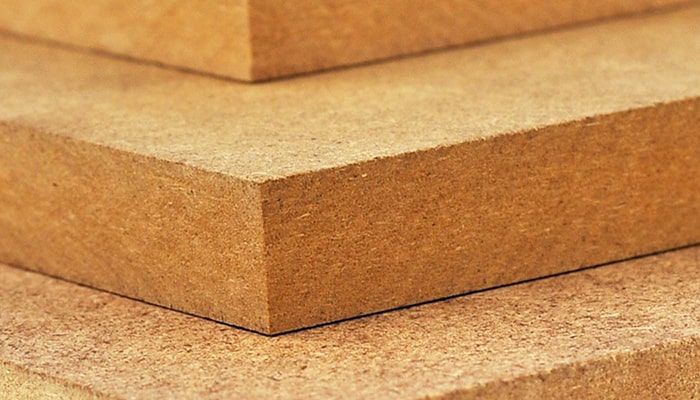

Fire Resistant MDF- and MDF variant that is more resistant to fire and heat, but certainly not fire-resistant. It is often used for structural elements in the home such as partition walls, where extra safety is quite welcome. It is usually red.
Ultra-light MDF- It is a newer variant of MDF that is approximately 30% lighter than the standard material. It’s great for components that need things like slots or dies but isn’t well suited for structural applications. MDF is bonded together by urea-formaldehyde resin. However, formaldehyde is a carcinogen and can be irritating to the mouth and nose.
1.2. Plywood
Plywood is another popular example of wood composite. There is a big difference between it and MDF, both in terms of use and construction of the material. Plywood is made from peeled logs; logs are cut to produce veneer. They are then glued together in layers with an adhesive, with a spiral groove.
Because plywood has twisted wood grains on each layer. The majority of plywood in the low to mid-range segment is made with alternating 90-degree angles. While the more advanced types of plywood often move in an increment of 45 degrees to increase the durability of the board.
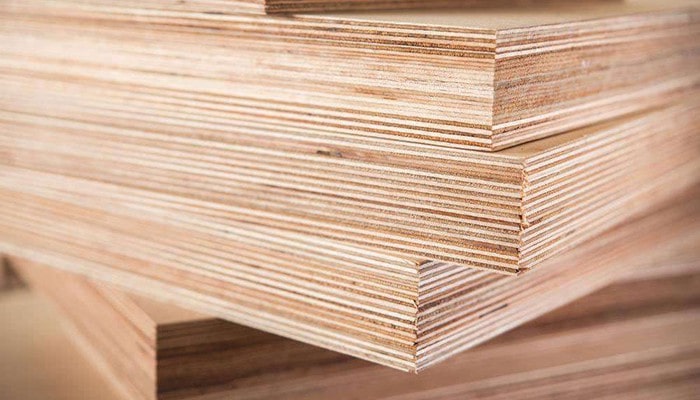

The maximum strength of a piece of wood is given by and in the direction of the grain. So, by rotating the direction of the particle, maximum strength can be achieved in multiple directions.
Popular types of plywood:
- Grade N- No nicks on the surface and fine sanded. This finish is mainly used when someone wants the wood grain to be visible after their work is done.
- Grade A- It differs from Grade N plywood in that it is designed for a top coat finish and has a less natural surface finish.
- Grade B – Smooth but with visible or repaired flaws in the veneer surface in most cases.
- The C-Rougher grade is better than previous grades, with visible fixes allowed and knots up to 1 ½” in diameter. Grade C plywood is commonly used in the construction where it will be covered.
- Grade D Plywood- It is rough and unfinished, allowing knots up to 2 ½”.
- The plywood that you buy will usually have a label as a CD. This just shows that the faces are distinct from each other and they should be marked for most applications. The X in the symbol means moisture resistance.
2. Distinguish MDF and Plywood
2.1. Application
- The common application of MDF is in furniture. It doesn’t have the beauty of natural wood, but it’s often used as a frame in handcrafted upholstered furniture like couches. MDF does not absorb paint well, yet it is still used in tables and other sturdy furniture. Paint can also form a protective coating; MDF is very susceptible to moisture if you do not use a moisture-resistant type.
- Since MDF is naturally fire-resistant, it can also be used for architectural elements in the home. It creates a protective barrier in the event of a fire emergency. There are also a number of special MDF products for specific uses.
- Particle Boards – These MDF panels are fastened to look like they have a grooved profile. Bead is a decorative element, often used for things like half-wall covers to create striking texture. Slatwall- Slatwall is commonly used in-store displays. It comes preconfigured to work as a stand and rack with matching lanyards. Its use around the house is limited but some people use it as a storage solution in the garage or kitchen.

- MDF is not moisture resistant in places with high humidity, as it will draw water from the air without splashing. Even so, MDF is often used to create consumer bathrooms and kitchen cabinets. This material is often covered with a thin layer of wood veneer, which helps prevent water from escaping and gives the cabinet a more natural look.
- Since plywood is designed to maximize durability, with well-defined veins, it is much harder than MDF. As a general rule, plywood is more impact resistant than MDF. It is more elastic and tends to return to its original shape after impact if nothing breaks.
- Plywood is also reasonably durable. While it’s not as good as a hardwood board in that respect, it can last for decades with proper care. Plywood is also less dense than MDF so it is lighter and easier to handle.
2.2. Cost
- Compared to MDF plywood, Plywood is more expensive. How much more depends on the grade and type of wood. Plywood is still cheaper than most real woods, especially hardwoods.
- MDF costs much more competitive than Plywood.

3. A1 Plywood – Prestigious and Quality Plywood Factory
A1 Plywood is committed to the prestige and quality of products, ensuring that Plywood panels are always delivered to customers according to requirements and designs.
We own a direct furniture factory in Vietnam, with a team of skilled carpenters, each product is made carefully from the stage of choosing boards to construction and installation.
The factory accepts orders to produce Plywood boards based on the correct sizes and measurements as required, and delivery on time.
The above is the difference between MDF and plywood, basing on it customer can choose the suitable wood.
Related keywords: what is the difference between plywood mdf and particleboard, difference between mdf and ply, is mdf or plywood better, which is best mdf or plywood, why use mdf instead of plywood, the difference between mdf and plywood and osb, the difference between mdf and plywood and mdf.